China 16A 240V AC EV Charging Gbt Socket - Manufacturer, Supplier, Factory
Rated: 16A 250V AC
Cable Length: Customized
Working temperature: -30℃~+50℃
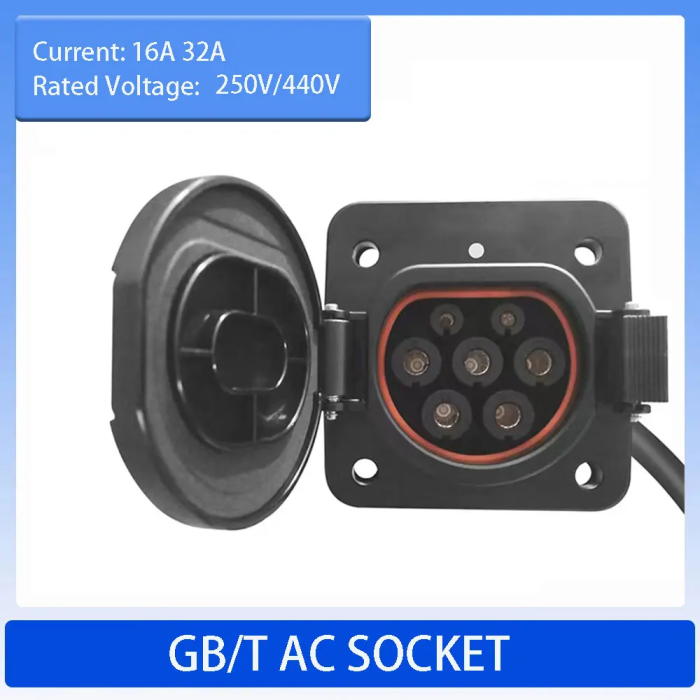

Features of AC EV Charging GBT Socket
- Proven robust design
- Lowest insertion force in the market
- High reliability (guarantee for a minimum of 10 000 mating cycles)
- Silver plated contacts
- Several customization options

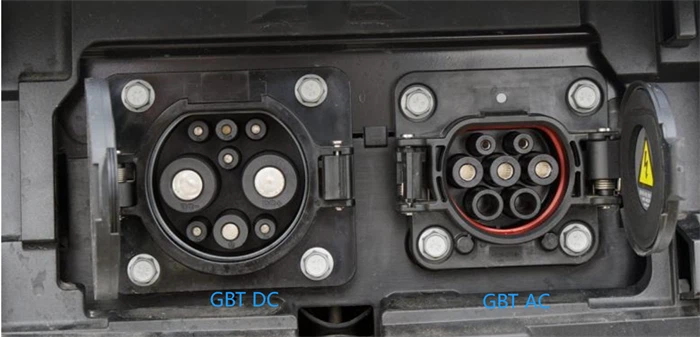
What Is The Difference of GBT AC Charging Socket and GBT DC Charging Socket?
The difference between GBT AC charging sockets and GBT DC charging sockets lies in their design, power handling capabilities, and intended use. Here's a detailed comparison:
1. Power Type and Conversion
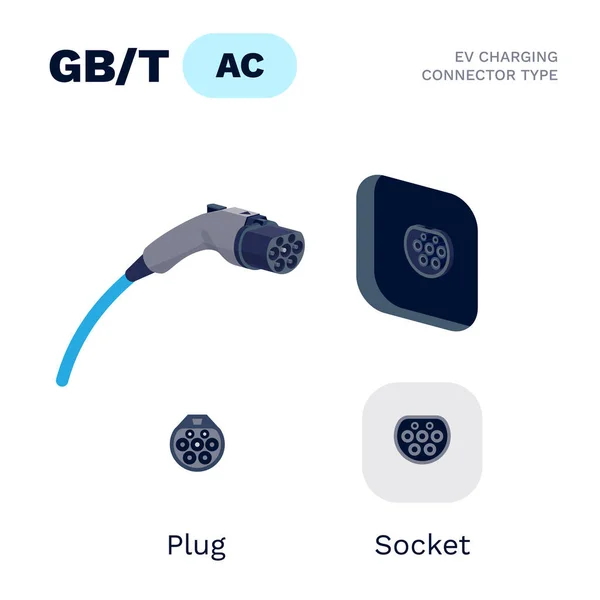
GB/T AC Charging Socket (GB/T 20234.2):
Designed to transfer alternating current (AC) from the grid to the electric vehicle (EV).
The AC is converted to DC by the vehicle's onboard charger.
Typically used for slower charging, as the power is limited by the onboard charger's capacity.
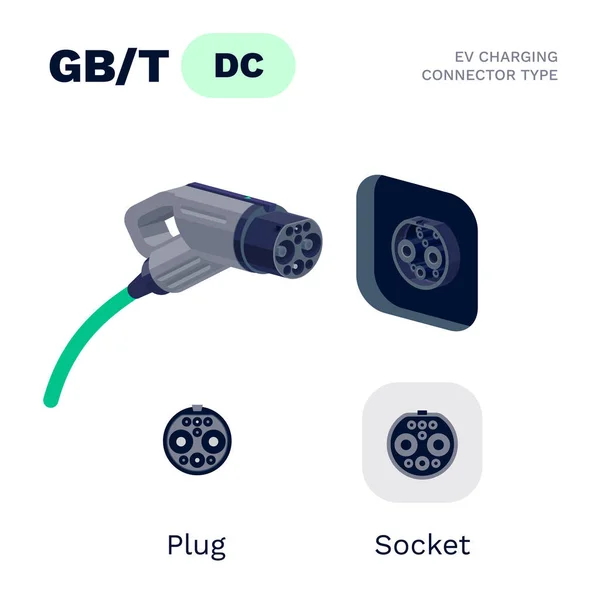
GB/T DC Charging Socket (GB/T 20234.3):
Designed to directly transfer direct current (DC) from the charging station to the vehicle’s battery.
The power is already converted from AC to DC inside the charging station, so the vehicle’s onboard charger is bypassed.
Used for fast charging, allowing higher power transfer and faster charging times.
2. Connector Design
GB/T AC Charging Socket:
Simpler design with fewer pins compared to DC sockets.
Typically includes five pins for AC power transfer, grounding, and communication between the vehicle and charging station.
Smaller, designed to handle lower current (up to 22 kW) compared to DC connectors.
GB/T DC Charging Socket:
Bulkier design with larger pins to handle higher current and voltage.
Typically includes seven or more pins, with separate large pins for positive and negative DC power lines, and additional smaller pins for communication and grounding.
Designed to support much higher power levels (50 kW to 350 kW), which enables faster charging speeds.
3. Power Handling
GB/T AC Charging Socket:
Supports single-phase or three-phase AC.
Power delivery is typically up to 7.4 kW for single-phase and up to 22 kW for three-phase AC.
Suitable for slower, overnight charging or use in residential settings.
GB/T DC Charging Socket:
Supports high-power DC charging.
Power output ranges from 50 kW to 350 kW or more, depending on the charging station.
Designed for rapid charging, typically used in public fast-charging stations.
4. Use Case
GB/T AC Charging Socket:
Primarily used in residential or low-power public settings, such as homes, offices, and parking lots.
Ideal for longer charging durations when speed is not a priority, like overnight charging.
GB/T DC Charging Socket:
Primarily used at public fast-charging stations, especially on highways and for commercial use.
Ideal for quick recharges, such as when traveling long distances or when fast turnaround is needed.
5. Safety Features
GB/T AC Charging Socket:
Includes standard safety measures like grounding, insulation monitoring, and communication protocols to ensure the charging process is safe.
Designed for lower voltage and current, so the safety requirements are simpler compared to DC charging.
GB/T DC Charging Socket:
Equipped with additional safety features to manage high-power charging, including temperature monitoring, cooling systems (for some high-power systems), and more robust grounding and insulation requirements.
Must handle higher voltage and current, so the design and materials are more robust to prevent overheating or electrical hazards.
6. Physical Size and Structure
GB/T AC Charging Socket:
Generally smaller and lighter due to the lower power levels it handles.
Simpler pin configuration, making it easier to install in residential or urban areas.
GB/T DC Charging Socket:
Larger and heavier to accommodate the thicker, more durable cables and larger pins needed for higher power transfer.
Designed for industrial or commercial use, typically in public fast-charging networks.
Hot tags: #gbt #gbt socket #manufacturers #factories












 Senku ,Bake
Senku ,Bake Senku
Senku